Blockchain technology has gained significant attention and adoption across various sectors due to its ability to offer secure, transparent, and decentralized solutions. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore what is blockchain, how it works, its benefits, and its diverse applications.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that enables the secure and transparent recording of transactions across multiple computers. Each transaction is recorded in a block, and these blocks are linked together in a chain, hence the name blockchain. This technology ensures that the information is immutable and tamper proof.
Blockchain was initially developed as the underlying technology for Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency. However, its potential extends far beyond digital currencies. Today, blockchain is being explored and implemented in various fields, including finance, supply chain management, healthcare, and more.
Key Takeaway
- Blockchain is a type of shared database that stores information differently from a typical database by organizing data into blocks linked together through cryptography.
- You can store various types of information on a blockchain, but its most common use has been as a transaction ledger.
- For example, in the case of Bitcoin, the blockchain is decentralized, meaning no single person or group has control; instead, control is distributed among all users collectively.
- In a decentralized blockchain, once data is entered, it cannot be changed. Take Bitcoin, for instance: every transaction is permanently recorded and visible to everyone.
How Does Blockchain Work?
To mastery how blockchain works, it’s essential to grasp the following concepts:
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
In a traditional centralized system, a single entity controls the database. In contrast, blockchain uses a distributed ledger that is maintained by a network of computers (nodes). Each node has a copy of the entire ledger, ensuring transparency and security.
Consensus Mechanisms
Blockchain relies on consensus mechanisms to validate and agree on the transactions added to the ledger. The most common consensus mechanisms are:
- Proof of Work (PoW): Nodes solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and create new blocks. This process requires significant computational power.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Validators are chosen based on the number of tokens they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral. This method is more energy efficient than PoS.
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): Token holders elect a small group of delegates to validate transactions and create blocks on their behalf.
Cryptographic Hashing
Each block in the blockchain contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, ensuring the chain’s integrity. Any alteration in a block’s data would change its hash, making it evident that tampering has occurred.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automatically execute actions when predefined conditions are met, enabling trustless transactions without intermediaries.
Key Components of Blockchain
Understanding the key components of blockchain technology is crucial to grasp its functionality fully. These components include:
Blocks
A block is a data structure that stores transaction details. Each block consists of:
- Header: Contains metadata, including the previous block’s hash, timestamp, and a nonce (a random number used in PoW).
- Data: Contains the actual transaction information.
Nodes
Nodes are individual computers that participate in the blockchain network. They validate and relay transactions and can be categorized as:
- Full Nodes: Store the entire blockchain and validate transactions independently.
- Light Nodes: Store only a portion of the blockchain and rely on full nodes for validation.
Transactions
Transactions are the operations recorded on the blockchain. They represent the transfer of assets or information between parties and must be validated by the network before being added to a block.
Ledger
The ledger is a record of all transactions in the blockchain. It is distributed across all nodes in the network, ensuring transparency and security.
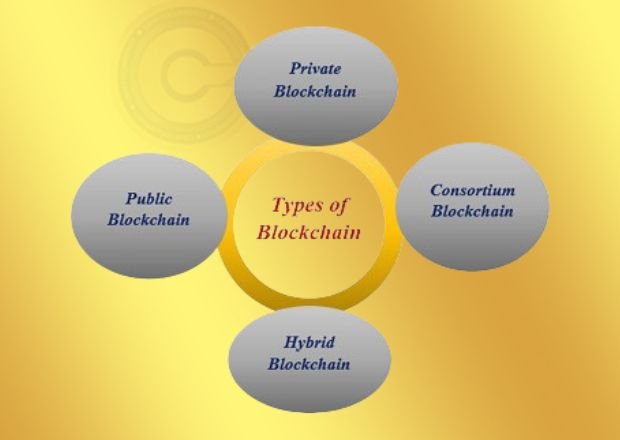
Types of Blockchain
Blockchain technology can be categorized into several types based on their structure and use cases:
Public Blockchain
Public blockchains are open to anyone and are fully decentralized. Bitcoin and Ethereum are prime examples of public blockchains. They rely on consensus mechanisms like PoW or PoS to validate transactions.
Private Blockchain
Private blockchains are restricted to a specific group of participants and are usually used by organizations for internal purposes. They offer more control over the network but are less decentralized than public blockchains.
Consortium Blockchain
Consortium blockchains are managed by a group of organizations rather than a single entity. They offer a balance between decentralization and control, making them suitable for industry collaborations.
Hybrid Blockchain
Hybrid blockchains combine elements of both public and private blockchains, allowing for controlled access to specific data while maintaining some level of decentralization.
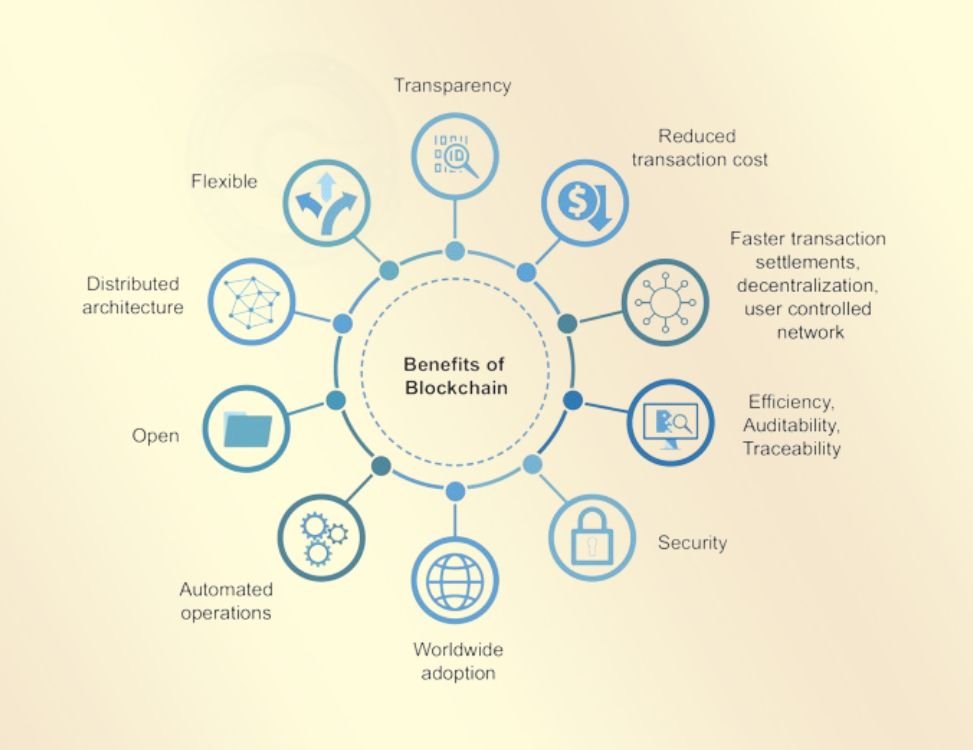
Benefits of Blockchain
Blockchain technology offers numerous benefits that make it attractive for various applications:
Transparency
Blockchain provides a transparent record of all transactions, which can be viewed and verified by all participants in the network. This transparency reduces the risk of fraud and enhances trust.
Security
The decentralized nature of blockchain, combined with cryptographic hashing, makes it highly secure. Altering any information on the blockchain requires consensus from the majority of the network, making tampering virtually impossible.
Immutability
Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This immutability ensures the integrity of the data and provides a reliable audit trail.
Efficiency
Blockchain can streamline processes by eliminating intermediaries and reducing the time required for transactions. Smart contracts further enhance efficiency by automating tasks based on predefined conditions.
Cost Savings
By reducing the need for intermediaries and automating processes, blockchain can significantly lower operational costs for businesses.
Blockchain Applications
Blockchain technology is being applied in various industries, transforming traditional processes and creating new opportunities:
Finance
In the financial sector, blockchain is revolutionizing the way transactions are conducted. It enables faster, cheaper, and more secure cross-border payments, reduces fraud, and enhances transparency. Cryptocurrencies, decentralized finance (DeFi), and tokenization of assets are some notable applications.
Supply Chain Management
Blockchain provides end-to-end visibility in supply chains, enabling the tracking of goods from their origin to the final destination. This transparency helps in reducing fraud, ensuring product authenticity, and improving efficiency.
Healthcare
In healthcare, blockchain is used to securely store and share patient records, ensuring data privacy and integrity. It also facilitates the tracking of pharmaceuticals, reducing the risk of counterfeit drugs.
Real Estate
Blockchain simplifies real estate transactions by providing a transparent and immutable record of property ownership. It reduces the need for intermediaries, speeds up transactions, and lowers costs.
Voting Systems
Blockchain-based voting systems enhance the security and transparency of elections. They provide a tamper-proof record of votes, ensuring the integrity of the electoral process.
Intellectual Property
Blockchain helps in protecting intellectual property by providing a secure and transparent record of ownership and licensing. It ensures that creators receive proper credit and compensation for their work.
Internet of Things (IoT)
In the IoT sector, blockchain enables secure and transparent communication between devices. It enhances the security of IoT networks and facilitates automated processes through smart contracts.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its numerous benefits, blockchain technology faces several challenges and limitations:
Scalability
Blockchain networks, especially those using PoW, can struggle with scalability issues. The process of validating and adding transactions can be slow and resource-intensive, limiting the number of transactions that can be processed per second.
Energy Consumption
Consensus mechanisms like PoW require significant computational power, leading to high energy consumption. This environmental impact is a major concern for the widespread adoption of blockchain.
Regulatory Uncertainty
The regulatory landscape for blockchain and cryptocurrencies is still evolving. Uncertainty and varying regulations across different jurisdictions can hinder the adoption and implementation of blockchain solutions.
Privacy Concerns
While blockchain provides transparency, it can also raise privacy concerns. Public blockchains make transaction details visible to all participants, which may not be suitable for applications requiring confidentiality.
Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating blockchain with existing legacy systems can be complex and costly. Organizations need to invest in new infrastructure and train personnel to manage and operate blockchain-based solutions.
Future of Blockchain
The future of blockchain technology looks promising, with ongoing developments and innovations addressing current challenges and expanding its applications. Some key trends to watch include:
Layer 2 Solutions
Layer 2 solutions, such as the Lightning Network for Bitcoin and Ethereum’s Optimistic Rollups, aim to improve scalability by processing transactions off the main blockchain. These solutions can significantly increase transaction throughput and reduce fees.
Green Blockchain Initiatives
Efforts are being made to develop more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms and green blockchain initiatives. Proof of Stake and other alternatives to Proof of Work are gaining traction to address environmental concerns.
Interoperability
Interoperability between different blockchain networks is becoming increasingly important. Projects like Polkadot and Cosmos are working on enabling seamless communication and data exchange between blockchains, fostering a more connected ecosystem.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi is a rapidly growing sector within the blockchain space, offering financial services without traditional intermediaries. The development of new DeFi protocols and platforms is expected to continue, providing users with more options for lending, borrowing, and trading assets.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
NFTs have gained significant attention for their ability to represent unique digital assets. The use of NFTs is expanding beyond art and collectibles to include gaming, real estate, and intellectual property.
Government and Enterprise Adoption
Governments and enterprises are increasingly exploring blockchain for various use cases, from digital identity and supply chain management to voting systems and regulatory compliance. This adoption is expected to drive further innovation and mainstream acceptance of blockchain technology.
Quantum Computing
The advent of quantum computing poses both challenges and opportunities for blockchain. While quantum computers could potentially break current cryptographic algorithms, they also offer the potential for developing more secure and efficient blockchain solutions.
Comparison of Blockchain Types
| Feature | Public Blockchain | Private Blockchain | Consortium Blockchain | Hybrid Blockchain |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Open to everyone | Restricted access | Limited to consortium members | Combination of both |
| Decentralization | High | Low | Moderate | Varies |
| Transaction Speed | Generally slower | Faster | Faster | Varies |
| Security | High | Depends on implementation | Depends on implementation | Varies |
| Use Cases | Cryptocurrencies, DeFi | Internal business processes | Industry collaborations | Varied applications |
This table provides a clear comparison of the different types of blockchains, highlighting their features and use cases.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is transforming the way we conduct transactions, manage data, and interact with digital systems. Its decentralized, transparent, and secure nature offers numerous benefits across various industries. While there are challenges to overcome, ongoing advancements and innovations continue to drive the growth and adoption of blockchain. As we look to the future, blockchain holds the promise of creating more efficient, secure, and inclusive digital ecosystems.
In summary, understanding blockchain technology and its potential applications is crucial for staying ahead in the evolving digital landscape. As blockchain continues to mature, it will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of numerous sectors, offering new opportunities and transforming traditional processes.


